
微信号:weixin888
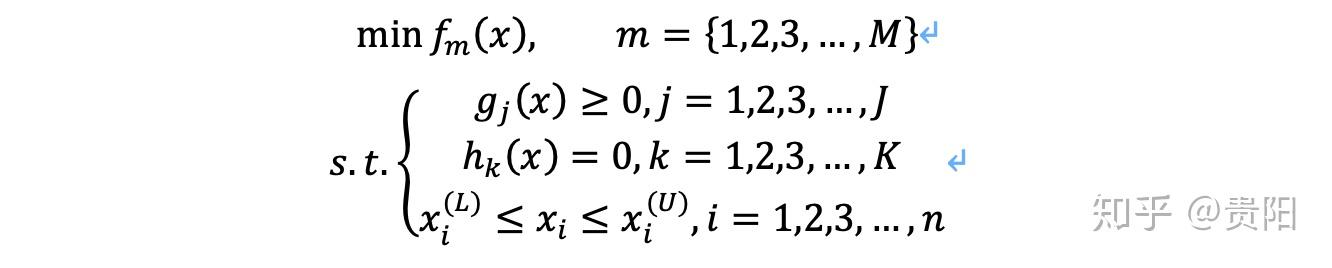
具体含义
帕累托最优是指资源分配的一种理想状态。给定固有的一群人和可分配的资源,如果从一种分配状态到另一种分配状态的变化中,在没有使任何人情况变坏的前提下,使得至少一个人变得更好,这就是帕累托改善。帕累托最优状态就是不可能有更多的帕累托改善的状态;换句话说,不可能在不使得任何其他人受损失的情况下改善某些人的情况。
抽象概念理解
当 和
满足如下条件时,称
支撑
:
1. 对于所有目标函数 不比
差
2. 至少在一个目标函数上, 严格比
要好
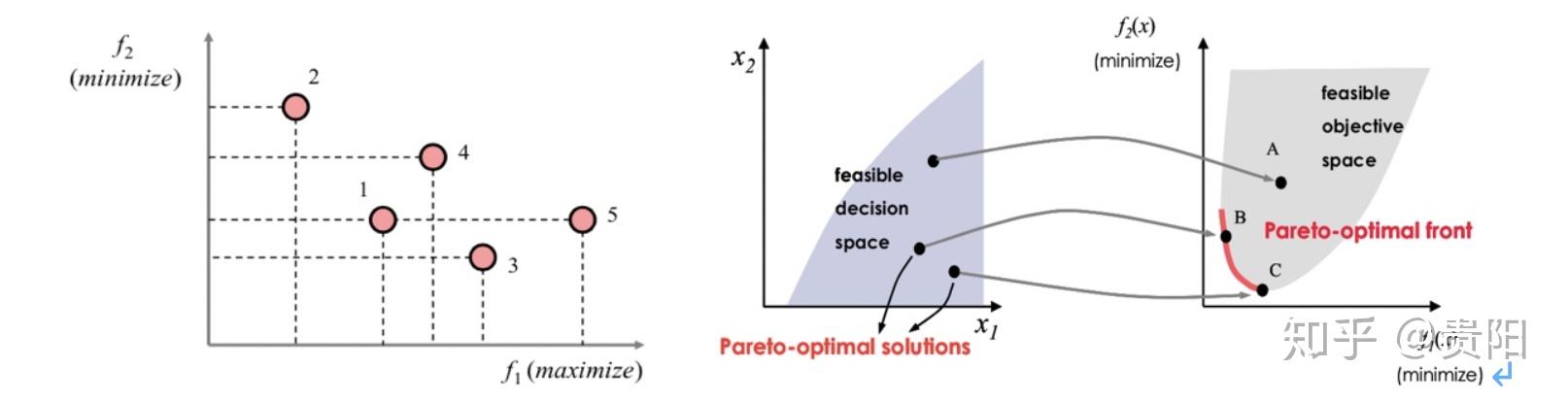
具体解释上图中的含义:
当一个解集中任何一个解都不能被集合中其他解支配,那么称该解集为不可支配解集。
所有可行解集中的不可支配解集被称为帕累托最优解集。
帕累托最优解集的边界(Boundary)被称为帕累托最优前沿面。
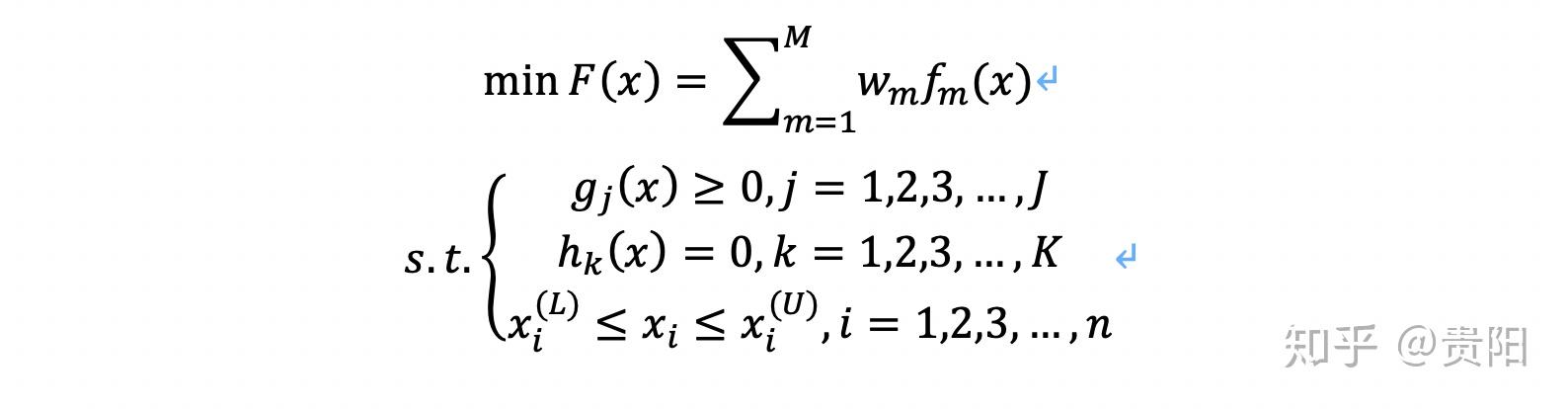
采用线性加权法,其中权重代表了每个目标函数的重要程度。但是,很难设定一个权重向量能够去获得帕累托最优解;并且在一定非凸情况不能够保证获得帕累托最优解。
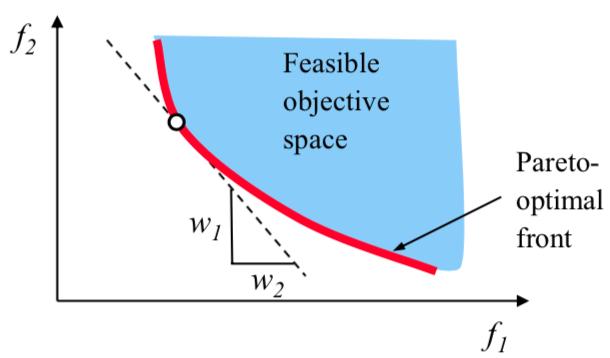

这里,只保留了一个目标函数,其他的目标函数被设定的值约束。能够应用到凸函数和非凸函数场景下。缺点:函数需要精心选择,需要独立目标函数的最小值或最大值之内。(Keep as an objective
, Treat
as a constraint
)
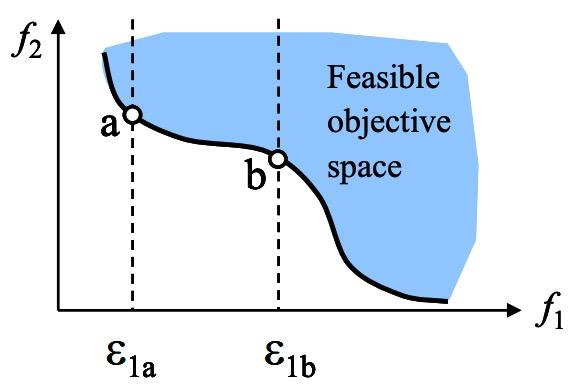

Weighted Teche by Cheff Metric能够保证获得所有帕累托最优解。缺点:需要有每个函数最大值和最小值的先验知识;需要每个目标函数 的能够独立被找到;对于较小的p值,不一定保证所有能够获得所有帕累托最优解;随着p增加,问题会变得不可求导。
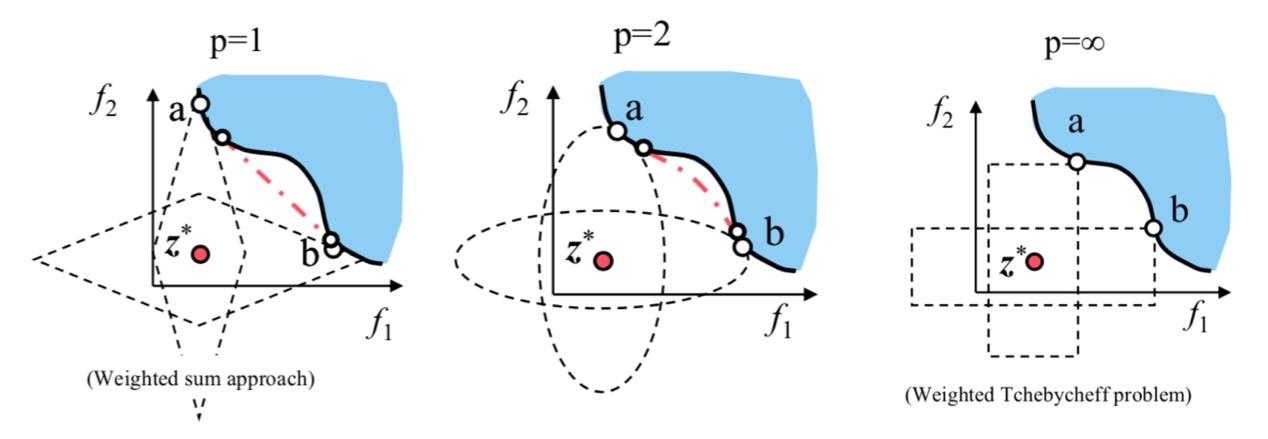
基于遗传算法的多目标优化就是利用遗传算法的原理来搜索帕累托最优前沿面。基本的流程如下:
jMetal优化框架的使用
jMetal是一个多目标优化的启发式搜索框架,由Java编写,具体的[Github地址在这里](https://github.com/jMetal/jMetal),具体的安装步骤,请读者自行百度进行使用吧。[官方提供的jMetal使用教程](https://github.com/jMetal/jMetalDocumentation),大家可以通过这个了解下具体的设计框架,这里我是使用两个例子对不同场景下的代码的使用进行编写。
Griewank函数优化
在数值优化领域,Greiwank Function经常作为优化函数,使用在优化领域。具体函数定义如下:
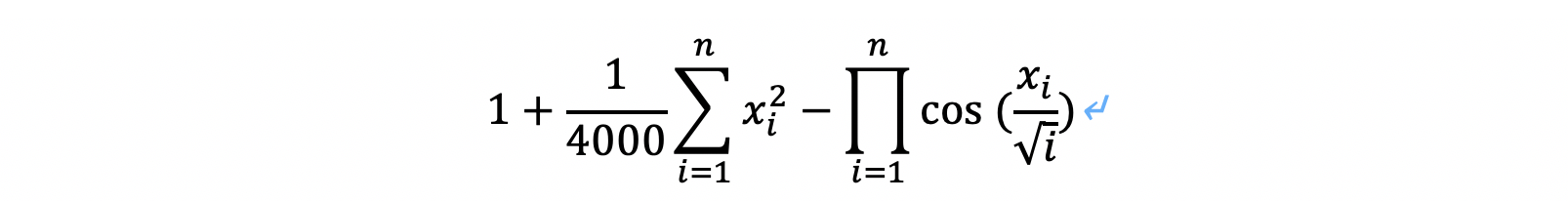
我们来可视化当 时具体的函数形态:
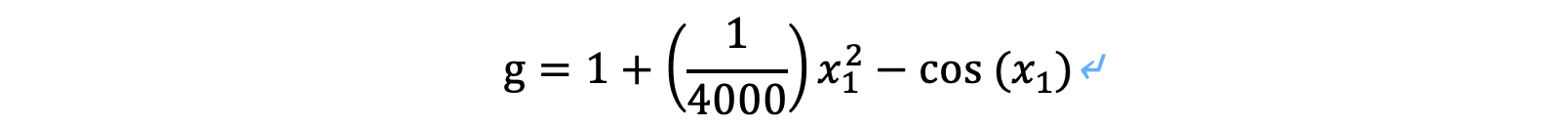
我们来可视化当 时具体的函数形态:
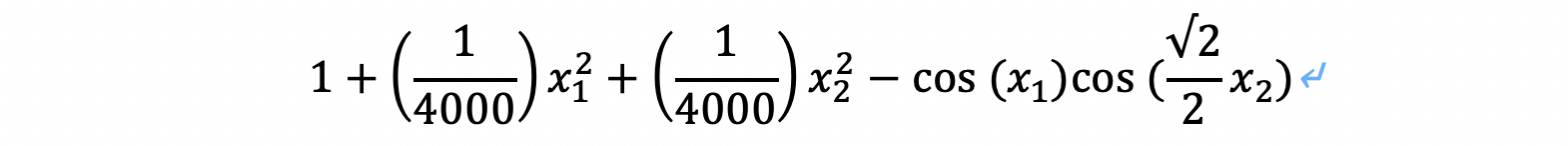

GriewankProblem.java 用来定义问题
import org.uma.jmetal.problem.impl.AbstractDoubleProblem;
import org.uma.jmetal.solution.DoubleSolution;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class GriewankProblem extends AbstractDoubleProblem {
public GriewankProblem(Integer numberOfVariables) {
setNumberOfVariables(numberOfVariables);
setNumberOfObjectives(1);
setName("GriewankProblem");
List<Double> lowerLimit = new ArrayList<>(getNumberOfVariables());
List<Double> upperLimit = new ArrayList<>(getNumberOfVariables());
for(int i=0;i<getNumberOfVariables();i++) {
lowerLimit.add(-600.0);
upperLimit.add(600.0);
}
setLowerLimit(lowerLimit);
setUpperLimit(upperLimit);
}
@Override
public void evaluate(DoubleSolution doubleSolution) {
int numberOfVariables = getNumberOfVariables();
double[] x = new double[numberOfVariables];
for(int i=0;i<numberOfVariables;i++) {
x[i] = doubleSolution.getVariableValue(i);
}
double sum = 0.0;
double mult = 1.0;
double d = 4000.0;
for(int var=0;var<numberOfVariables;var++) {
sum += Math.pow(x[var], 2.0);
mult *= (Math.cos(x[var]) / Math.sqrt(var + 1));
}
doubleSolution.setObjective(0, 1.0 / d * sum - mult + 1.0);
}
}
GriewankOptimization.java 用来定义问题
import insight.algo.optimization.problem.GriewankProblem;
import org.uma.jmetal.algorithm.Algorithm;
import org.uma.jmetal.algorithm.singleobjective.geneticalgorithm.GeneticAlgorithmBuilder;
import org.uma.jmetal.operator.CrossoverOperator;
import org.uma.jmetal.operator.MutationOperator;
import org.uma.jmetal.operator.SelectionOperator;
import org.uma.jmetal.operator.impl.crossover.SBXCrossover;
import org.uma.jmetal.operator.impl.mutation.PolynomialMutation;
import org.uma.jmetal.operator.impl.selection.BinaryTournamentSelection;
import org.uma.jmetal.problem.DoubleProblem;
import org.uma.jmetal.solution.DoubleSolution;
import org.uma.jmetal.util.AlgorithmRunner;
import org.uma.jmetal.util.fileoutput.SolutionListOutput;
import org.uma.jmetal.util.fileoutput.impl.DefaultFileOutputContext;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class GriewankOptimization {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int numberOfVariables = 1;
Algorithm<DoubleSolution> algorithm;
DoubleProblem problem = new GriewankProblem(numberOfVariables);
CrossoverOperator<DoubleSolution> crossoverOperator = new SBXCrossover(0.9, numberOfVariables);
MutationOperator<DoubleSolution> mutationOperator = new PolynomialMutation(1.0 / problem.getNumberOfVariables(), numberOfVariables);
SelectionOperator<List<DoubleSolution>, DoubleSolution> selectionOperator = new BinaryTournamentSelection<DoubleSolution>();
algorithm = new GeneticAlgorithmBuilder<>(problem, crossoverOperator, mutationOperator)
.setPopulationSize(200)
.setMaxEvaluations(25000)
.setSelectionOperator(selectionOperator)
.build();
AlgorithmRunner algorithmRunner = new AlgorithmRunner.Executor(algorithm).execute();
DoubleSolution solution = algorithm.getResult();
List<DoubleSolution> population = new ArrayList<>(1);
population.add(solution);
new SolutionListOutput(population)
.setSeparator("\ ")
.setVarFileOutputContext(new DefaultFileOutputContext("VAR.tsv"))
.setFunFileOutputContext(new DefaultFileOutputContext("FUN.tsv"))
.print();
}
}

MultiConstraintsProblem.java
import org.uma.jmetal.problem.DoubleProblem;
import org.uma.jmetal.solution.DoubleSolution;
import org.uma.jmetal.solution.impl.DefaultDoubleSolution;
import org.uma.jmetal.util.solutionattribute.impl.NumberOfViolatedConstraints;
import org.uma.jmetal.util.solutionattribute.impl.OverallConstraintViolation;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public class MultiConstraintsProblem implements DoubleProblem {
private List<Double> lowerBounds;
private List<Double> upperBounds;
private List<Function<Double[], Double>> objectiveFunction;
private List<Function<Double[], Double>> constraints;
private String name;
private OverallConstraintViolation<DoubleSolution> overallConstraintViolationDegree;
private NumberOfViolatedConstraints<DoubleSolution> numberOfViolatedConstraints;
public MultiConstraintsProblem() {
this.lowerBounds = new ArrayList<>();
this.upperBounds = new ArrayList<>();
this.objectiveFunction = new ArrayList<>();
this.constraints = new ArrayList<>();
this.name = "";
this.overallConstraintViolationDegree = new OverallConstraintViolation<>();
this.numberOfViolatedConstraints = new NumberOfViolatedConstraints<>();
}
public MultiConstraintsProblem addObjectiveFunction(Function<Double[], Double> objective) {
this.objectiveFunction.add(objective);
return this;
}
public MultiConstraintsProblem addConstraintFunction(Function<Double[], Double> constraint) {
this.constraints.add(constraint);
return this;
}
public MultiConstraintsProblem addVariable(double lowerBound, double upperBound) {
this.lowerBounds.add(lowerBound);
this.upperBounds.add(upperBound);
return this;
}
public MultiConstraintsProblem setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
return this;
}
@Override
public int getNumberOfVariables() {
return this.lowerBounds.size();
}
@Override
public int getNumberOfObjectives() {
return this.objectiveFunction.size();
}
@Override
public int getNumberOfConstraints() {
return this.constraints.size();
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
@Override
public void evaluate(DoubleSolution solution) {
Double[] x = solution.getVariables().toArray(new Double[getNumberOfVariables()]);
IntStream.range(0, getNumberOfObjectives())
.forEach(i -> solution.setObjective(i, this.objectiveFunction.get(i).apply(x)));
if(getNumberOfConstraints() > 0) {
double overAllConstraintViolation = 0.0;
int violatedConstraints = 0;
for(int i=0;i<getNumberOfConstraints();i++) {
double violateDegree = this.constraints.get(i).apply(x);
if(violateDegree >= 0) {
overAllConstraintViolation += violateDegree;
violatedConstraints += 1;
}
}
this.overallConstraintViolationDegree.setAttribute(solution, overAllConstraintViolation);
this.numberOfViolatedConstraints.setAttribute(solution, violatedConstraints);
}
}
@Override
public DoubleSolution createSolution() {
return new DefaultDoubleSolution(this);
}
@Override
public Double getLowerBound(int i) {
return this.lowerBounds.get(i);
}
@Override
public Double getUpperBound(int i) {
return this.upperBounds.get(i);
}
}
MultiConstraintsOptimization.java
import insight.algo.optimization.problem.MultiConstraintsProblem;
import org.uma.jmetal.algorithm.Algorithm;
import org.uma.jmetal.algorithm.singleobjective.geneticalgorithm.GeneticAlgorithmBuilder;
import org.uma.jmetal.operator.CrossoverOperator;
import org.uma.jmetal.operator.MutationOperator;
import org.uma.jmetal.operator.SelectionOperator;
import org.uma.jmetal.operator.impl.crossover.SBXCrossover;
import org.uma.jmetal.operator.impl.mutation.PolynomialMutation;
import org.uma.jmetal.operator.impl.selection.BinaryTournamentSelection;
import org.uma.jmetal.solution.DoubleSolution;
import org.uma.jmetal.util.AlgorithmRunner;
import org.uma.jmetal.util.fileoutput.SolutionListOutput;
import org.uma.jmetal.util.fileoutput.impl.DefaultFileOutputContext;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class MultiConstraintsOptimization {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MultiConstraintsProblem problem = new MultiConstraintsProblem()
.setName("multi-constraints")
.addVariable(0.0, 1.0)
.addVariable(0.0, 1.0)
.addVariable(0.0, 1.0)
.addObjectiveFunction((x) -> -3 * x[0] + 2 * x[1] - 5 * x[2])
.addConstraintFunction((x) -> -1 * x[0] - 2 * x[1] + x[2] + 2)
.addConstraintFunction((x) -> -1 * x[0] - 4 * x[1] - x[2] + 4)
.addConstraintFunction((x) -> -1 * x[0] - x[1] + 3)
.addConstraintFunction((x) -> -4 * x[1] - x[2] + 6);
int numberOfVariables = 3;
CrossoverOperator<DoubleSolution> crossoverOperator = new SBXCrossover(0.9, numberOfVariables);
MutationOperator<DoubleSolution> mutationOperator = new PolynomialMutation(1.0/numberOfVariables, numberOfVariables);
SelectionOperator<List<DoubleSolution>, DoubleSolution> selectionOperator = new BinaryTournamentSelection<>();
Algorithm<DoubleSolution> algorithm = new GeneticAlgorithmBuilder<>(problem, crossoverOperator, mutationOperator)
.setPopulationSize(200)
.setMaxEvaluations(25000)
.setSelectionOperator(selectionOperator)
.build();
AlgorithmRunner algorithmRunner = new AlgorithmRunner.Executor(algorithm).execute();
DoubleSolution solution = algorithm.getResult();
List<DoubleSolution> poplation = new ArrayList<>(1);
poplation.add(solution);
new SolutionListOutput(poplation)
.setSeparator("\ ")
.setVarFileOutputContext(new DefaultFileOutputContext("/tmp/VAR.tsv"))
.setFunFileOutputContext(new DefaultFileOutputContext("/tmp/FUN.tsv"))
.print();
}
}我们是阿里云-日志服务团队(https://www.aliyun.com/product/sls),是针对实时数据一站式服务,在阿里集团经历大量大数据场景锤炼而成。提供日志类数据采集、消费、投递及查询分析功能,全面提升海量日志处理/分析能力,服务智能研发/运维/运营/安全等场景。这里有一些工大家试用的演示推广( https://promotion.aliyun.com/ntms/act/logdoclist.html )。欢迎大家使用钉钉扫码加入我们的用户群,里面有专业的同学为您解答。
